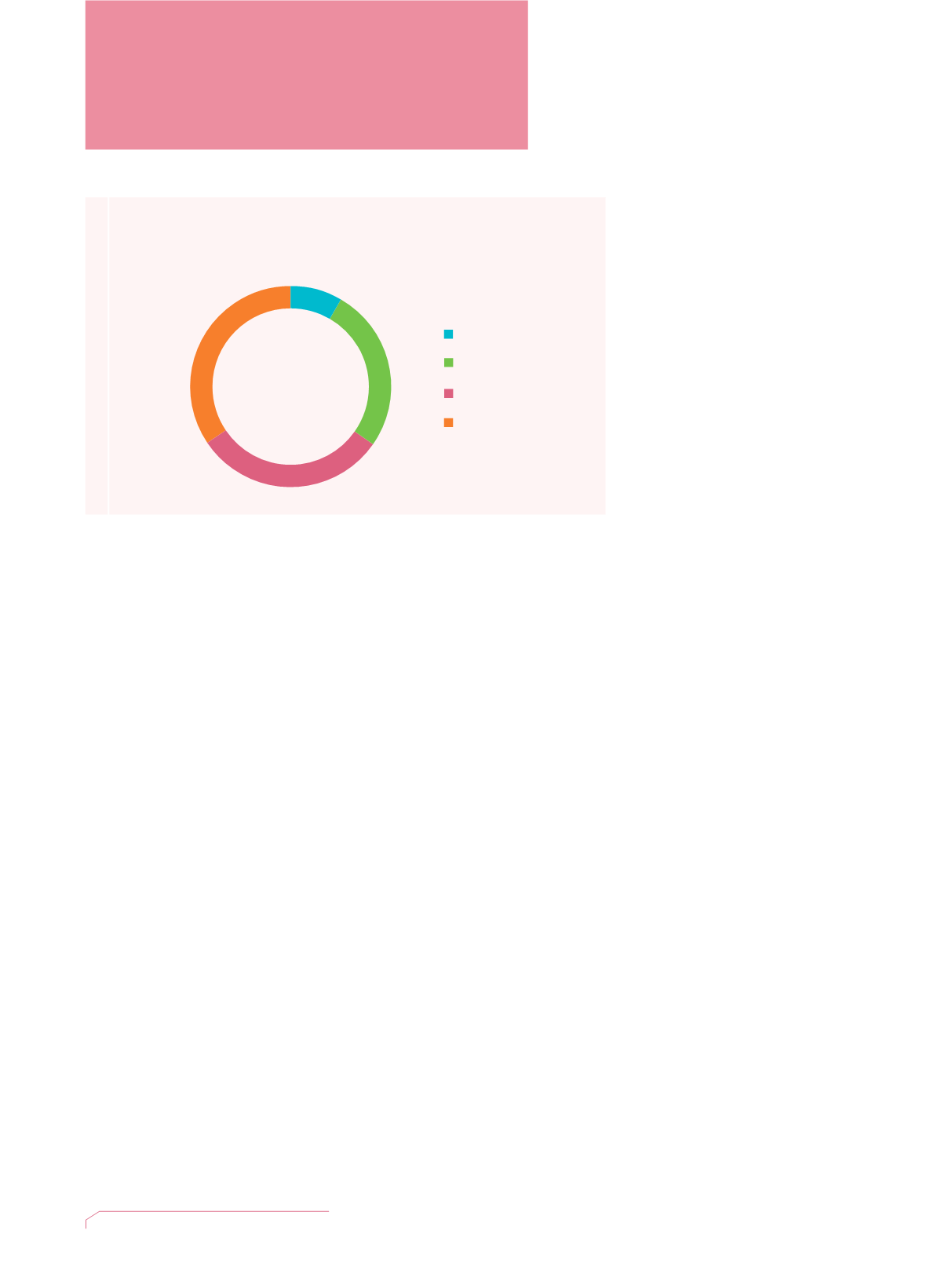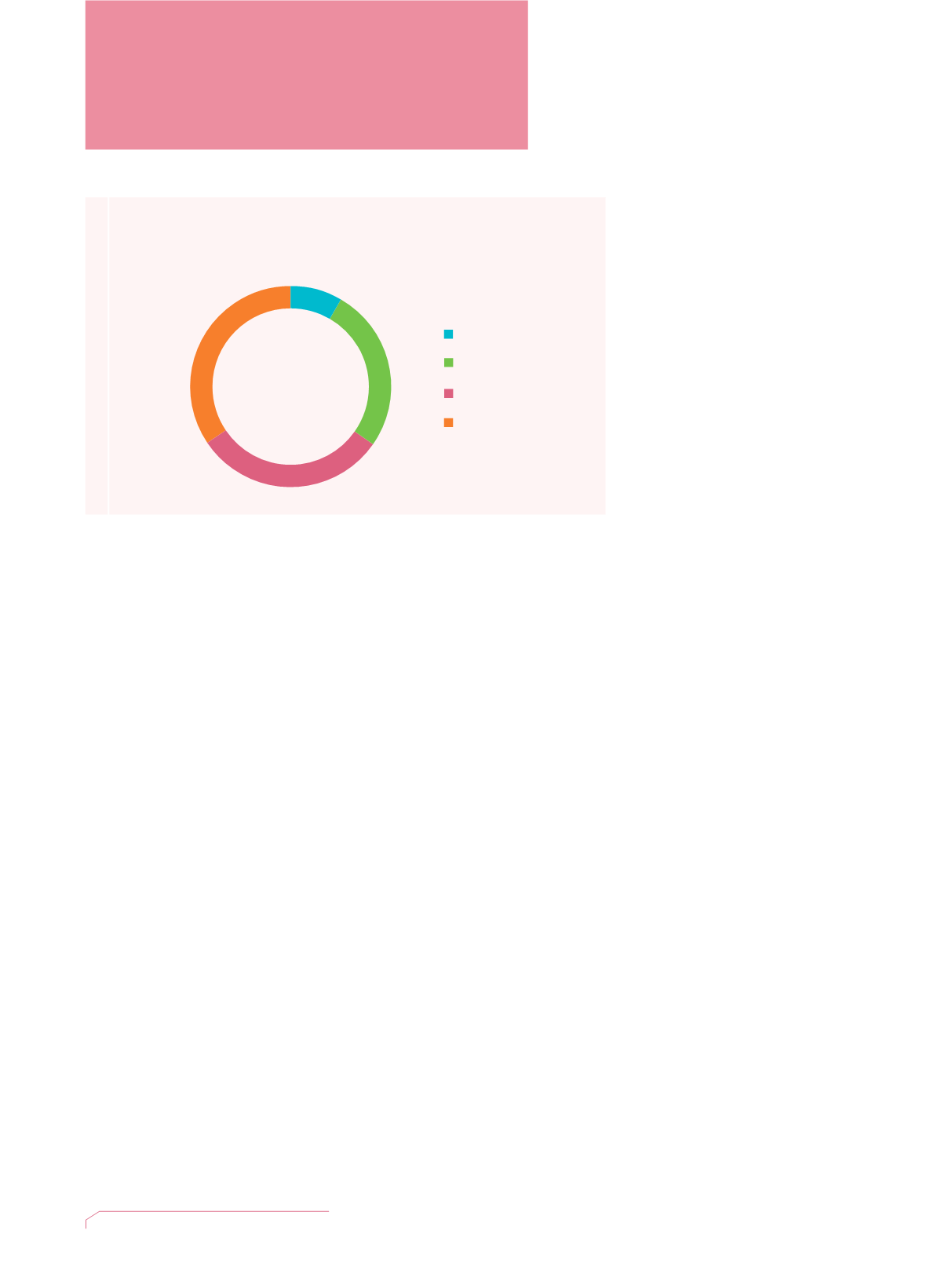
Hong Kong Housing Society Annual Report 2014
40
Elderly Housing and Care
長者房屋及護理
The Housing Society recognises the growing housing needs of the
ageing community in Hong Kong and is determined to make a special
contribution. In line with our tradition of being a laboratory in housing
services, we introduced a dimension of care into housing for the aged
under a segmentation model which is to provide differentiated services
to suit the diverse needs and expenditure patterns of the elderly in Hong
Kong, benchmarking international practices and with reference to our
own studies.
Under this approach, we have the ‘Ageing-in-Place’ (AIP) Scheme for
tenants in our own rental estates, the Senior Citizen Residences (SEN)
Scheme for elderlies in the middle-income group, and the Joyous Living
project for those of higher means.
In order to better orient our efforts, last year we conducted a study, with
the help of the Census and Statistics Department, on the income and
expenditure patterns of the elderly by economic stratum and age cohort,
as well as on their preferences for modes of housing and their ability to
pay in different scenarios.
In addition, we commissioned the Centre of Urban Studies and Urban
Planning of The University of Hong Kong to conduct a study on the
housing development trends in Hong Kong in view of our fast-growing
ageing population. Particular focus is made on the social and economic
profiles of the elderly, the housing situations they are in, their service
needs and the possible ways to meet them.
房協明白香港人口老化令長者房屋的需求
日趨殷切,故決意在這方面作出貢獻。我們
秉承房屋實驗室的傳統,以國際慣常做法
作為標準,再參考內部研究,將關顧的層
面帶入長者房屋,並根據市場的分割模式,
為香港不同需要及經濟能力的長者提供不同
服務。
在這模式下,我們為轄下的出租屋邨居民推
行「樂得耆所」計劃,亦為中等收入的長者
推出「長者安居樂」住屋計劃,另外並發展
「雋逸生活」項目,配合經濟能力較佳的長者
所需。
為了令我們更有效地針對目標市場,去年我
們展開一項研究,在統計處的協助下,按照
經濟能力及年齡組別分析長者的收入及支出
模式,了解他們在不同情況下對住屋形式的
喜好和消費能力。
另外,鑑於長者人口的急速增長,我們亦
委託了香港大學城市研究及城市規劃中心就
香港房屋發展的趨勢進行研究,重點分析
長者的社交、經濟及住屋狀況,以了解他們
對服務的需求及研究配合方案。
Age Profile of Housing Society Tenants
房協居民年齡分佈
as at 31 March 2014
截至二零一四年三月三十一日止
No. of Tenants
居民人數
Age
年齡
87,729
Total
總數
20-39 (26%)
40-59 (31%)
>60 (34%)
0-19 (9%)